By Kamaldeep Singh Sandhu
28 February 2019

The current situation
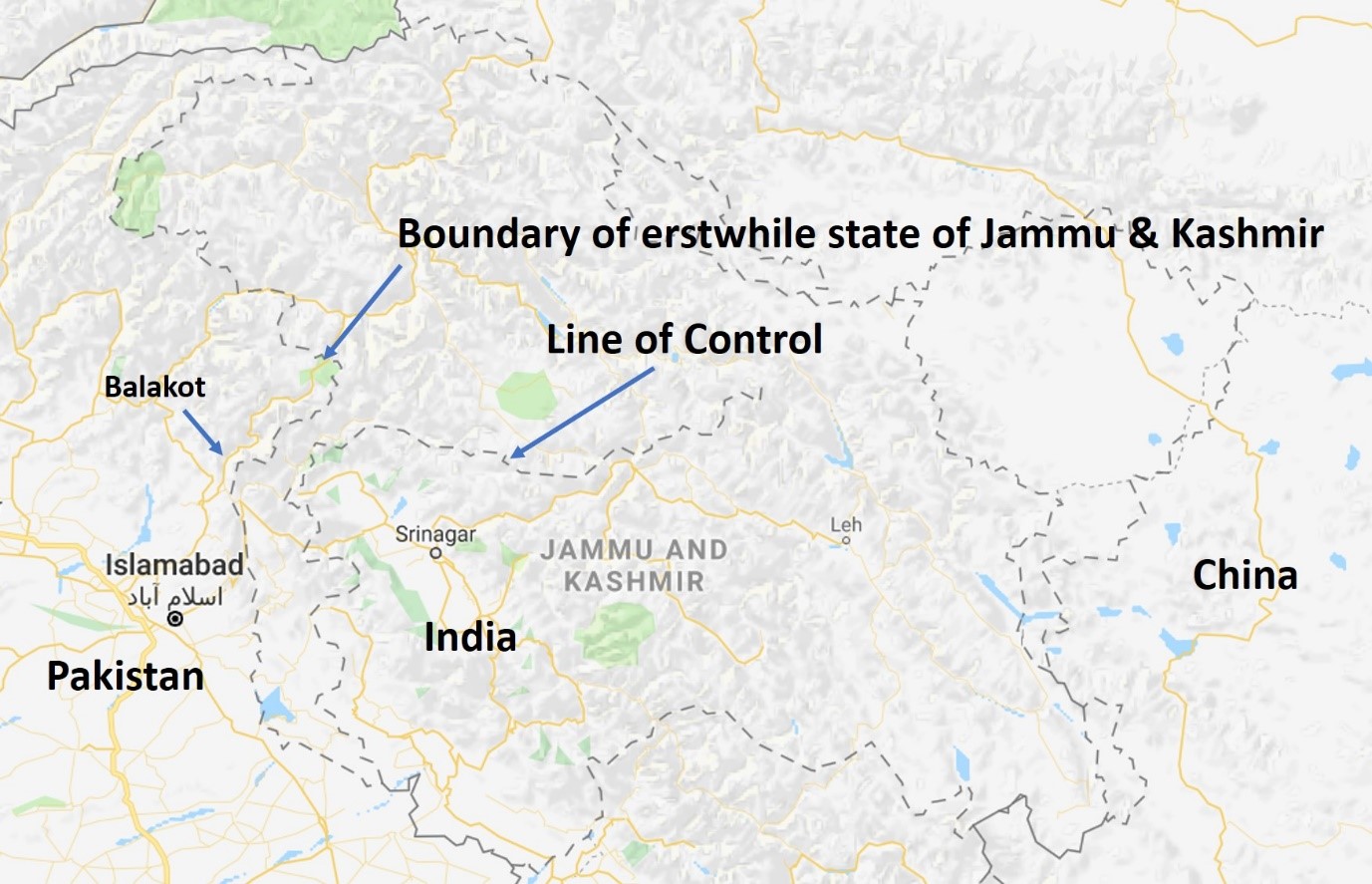
In the early hours of 26 February 2019, twelve Indian Mirage-2000 aircrafts carried out an air raid in Balakot, Pakistan, in retaliation of a suicide attack on India’s Central Reserve Police Force (paramilitary force used for internal security) convoy in Pulwama near Srinagar in Jammu & Kashmir which killed 44 soldiers on 14 Feb 2019. Jaish-e-Mohammad, a terrorist outfit known to have its bases in Pakistan, claimed the responsibility for the suicide attack. India contests that the raid was carried out on a JeM training camp and no civilian or military infrastructure was targeted; thus the raid is categorised it as a ‘non-military, pre-emptive strike’ and hence is not an act of war.
Pakistan’s military spokesperson Major General Asif Ghafoor, while acknowledging the strike, counter-claimed that the strike aircrafts were forced to a hasty withdrawal due to Pakistan Air Force’s (PAF) quick response and dropped the bombs in a hurry which fell in an open area with no casualties. Both sides claim credibility through impending details.
The current situation has showcased a new security paradigm in the asymmetric escalation of conflict or the escalation pyramid (normally called the escalation ladder). I chose to call it a ‘pyramid’ for a simple reason - as the rungs go higher, besides being alarming and dangerous, the retaliatory options become more and more limited to both the adversaries.

Background
Not having any conventional capability and under desperation to capture Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan started this vicious cycle at a sub-conventional level by sending the irregulars, the Afridis and Hazaraas from its North West Frontier Province, to capture the state of Jammu & Kashmir in 1947. After the success of Mujahedeen in Afghanistan in 1980s, which forced a Soviet withdrawal, the same model of insurgency has been used in Jammu & Kashmir since 1990. Slowly these non-state actors grew powerful and challenged the writ of the state itself. For instance, the terrorist outfit JeM carried out three attacks on Pakistani President Parvez Musharraf during his time in office. For the past few decades, any peace initiative by India or Pakistan has been followed by a terrorist attack in India which sets this escalatory cycle in motion. Lately, since the declaration of opening of the Kartarpur corridor by Pakistani Prime Minister Imran Khan, a terrorist attack such as Pulwama was predicted, given the pattern of such attacks .
India’s response has mostly been using its conventional infrastructure, demonstrated by ex-Brasstracks in 1986-87, the Operation Parakaram (Twin Peak crisis) in 2001-02, the Cold Start doctrine from 2004 onward and the surgical strikes in 2016. Yet, Pakistani mainland has not been attacked since the 1971 war. Even during the Kargil War, India refrained from crossing the Line of Control.
The Rubicon of Escalation?
Calling it the need of the hour, India crossed the Rubicon by hitting inside Pakistan territory. India had long argued that ‘restraint’ is not its weakness but a strategic necessity due to the risk of rapid escalation along the pyramid. With the September 2016 surgical strikes and now the Balakot air strikes, that policy is clearly out of the window. The problem with the escalation pyramid above is that while it is easy to climb up, it is difficult to climb down from one level to another, as elaborated below.
In response to India’s air raids, which was done using conventional assets, Indian security specialists speculate that as usual a retaliatory attack by Pakistan will most probably be using the non-state actors (in the sub-conventional spectrum). However, a sub-conventional response by Pakistan has to be plausibly denied and cannot be given any official recognition and hence will not satisfy the domestic population to which the narrative of ‘India as an enemy’ has been fed since 1947. In other words, there will be no face saving in front of the domestic audience constantly fed by the narrative of a “1000 years’ war with India” if the attack is not claimed and acknowledged by the state. On the other hand, if acknowledged, this will only feed India’s narrative of Pakistan being a terrorist sponsor state and will exacerbate Pakistan’s isolation in the international forums. It was only due to such dilemmas, Pakistani Military leadership managed to get away with 2016 surgical strikes by denying it altogether.
In the meantime, Prime Minister Modi’s government in India drew some political mileage by celebrating the surgical strikes as an annual event. Riding on the same success wave, India crossed the Rubicon by striking the Pakistani mainland. In addition, unlike before, the strikes have been immediately acknowledged by the Pakistan military.
This time nevertheless, Pakistan promised a retaliation. But, as experts claim that a conventional response from Pakistan is a non-starter because there are no viable targets in India that Pakistan can hit without carrying out an ‘act of war’. India claims that its air strikes were not an act of war since no military or civilian target was targeted or harmed. Hence, in retaliation, Pakistan can only increase firing along the Line of Control, which has already started. Pakistan’s military also called for a meeting of its National Command Authority, the apex body in charge of Pakistan’s nuclear arsenals which signals the usual ‘nuclear rattling’. As the escalation pyramid suggests, this is a next logical escalatory step which will draw lots of international attention and mediation that will call for de-escalation of the situation. Anything else will only cause more harm, as shown by downing of two fighter aircrafts, one from each side and capture of an Indian pilot by Pakistan on the morning of 27 Feb 2019. The conflict might continue in such duels and skirmishes but further escalation is least likely as explained in the accompanying piece.
The urgency of escalation
What is the urgency of escalation? This can be explained by the rapid spread of news on social media to a hysterical population, fed by frenzy media asking for revenge which puts pressure on those in power to act fast - a government for which time is running out due to an upcoming election and a powerful military running the affairs on the other side, which needs an immediate face saving to retain its legitimacy to remain in charge. Hence the retaliations are necessary, urgent and must be escalatory in order to dominate the deterrence.
Beyond all this…
While addressing an election rally immediately after the air strikes, Prime Minister Modi assured the audience that the ‘country is in safe hands’. Historical evidence suggests that this escalatory cycle of revenge and retaliation has not brought safety in the sub-continent. The violence has only killed soldiers and civilians on both sides. Further escalation will take it to the brink of devastation.
So what purpose does it serve? Pacifists claim that it certainly helps keep the belligerents on both sides of the border stay in power by giving a sense of honour and pride to the populations fed with the misconstrued sense of nationalism. It boosts the morale of the armed forces of the side which strikes last and dominates. It also distracts the electorate from other social and developmental issues, such as poverty, sanitation, lack of jobs and keeps it ‘rallied round the flag’.
Realists claim that this was the need of the hour since the public opinion of a thriving democracy demanded it. Indian Generals have long believed that there is enough space below the nuclear threshold where a limited conventional war with Pakistan can be fought and have backed calling Pakistan’s nuclear bluff on several occasions. Having just done that, has India finally crossed the Rubicon of escalation and set a wrong precedence? At the moment the answer depends upon lot of things including the treatment and fate of the captured pilot, Wing Commander Abhinandan. In the meantime and amidst this debate, a belligerent game of revenge and retaliation is being played for honour and dominance where the skies are devoid of civil flights and the military radars are churning.
Kamaldeep Singh Sandhu is a doctoral student at the Defence Studies Department, King’s College London and a Senior Editor for Strife. His research interests include South Asian security, military culture and defence diplomacy. An alumnus of National Defence Academy, Pune and Army War College, Mhow, he has served as an officer with the Indian army’s Parachute Regiment for ten years. You can follow him on Twitter @kamal_sandhu78.
Image source: https://www.mudspike.com/dcs-world-mirage-2000-c-hunter-is-here/
Kamaldeep Singh Sandhu
Kamaldeep Singh Sandhu is a PhD Candidate in the Defence Studies Department at King’s College London. His research interests include South Asian security, military culture, and defence diplomacy. An alumnus of National Defence Academy, Pune, Army War College, Mhow and The Royal Military Academy Sandhurst, he has served as an Officer with the Indian army’s Parachute Regiment for ten years and currently serves as an Officer in the Reserve Army, UK. You can find him on Twitter at kamal_sandhu78.