By: Jack Curran-Persell

Hebatalla Taha is a Research Analyst for the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) in London where she focuses on the Middle-East and North Africa.
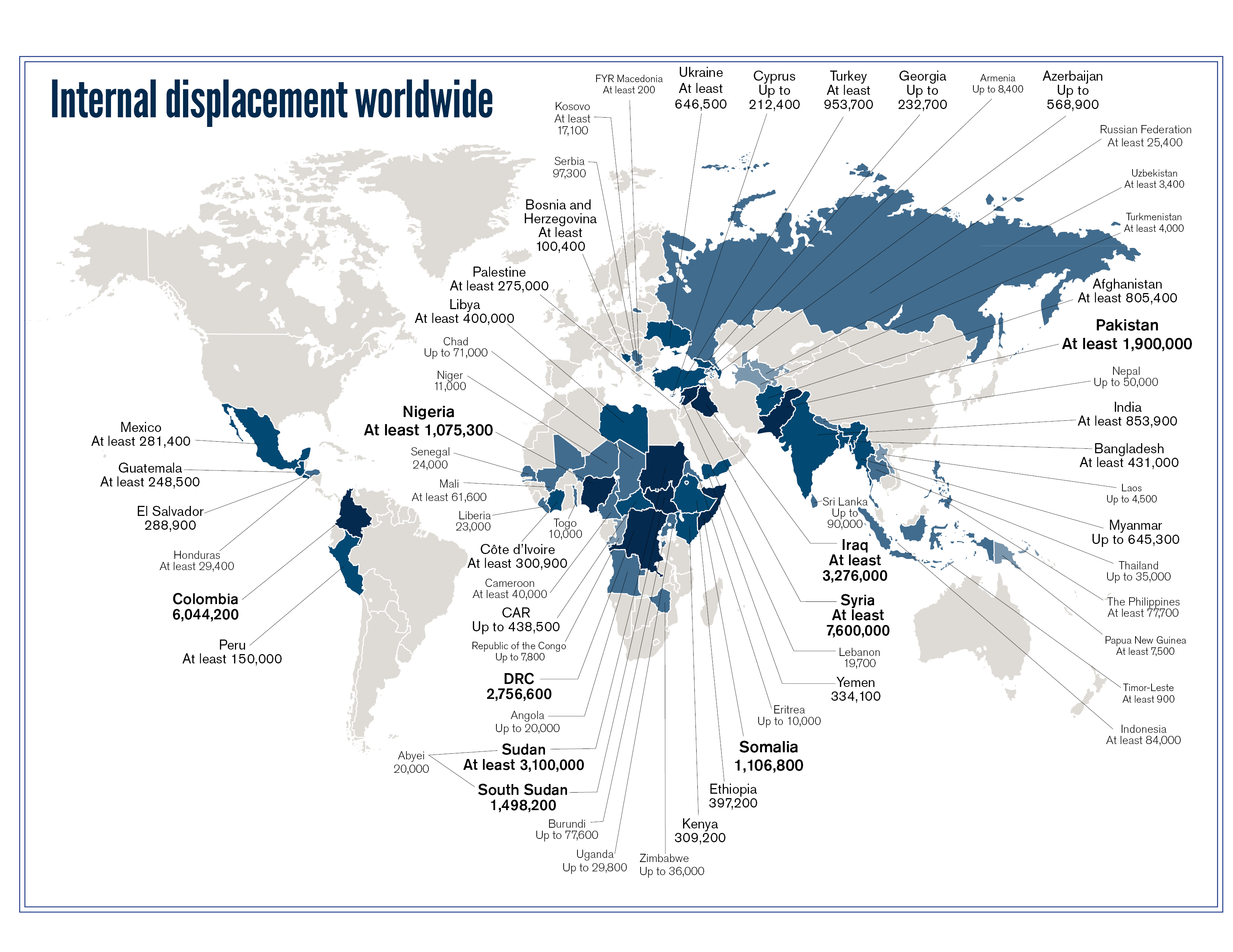
Jack Curran-Persell: Earlier this month, you wrote a very interesting article for IISS on the situation for IDPs in Iraq. With the UN estimating over 3 million Iraqis have been displaced, could you explain what the current situation is like for these people?
Hebatalla Taha: Conditions for IDPs in Iraq have been dire. In the article, I focused on how ISIS in particular limits the movement of civilians in areas under its control, but there are actually various armed groups and actors across Iraq that make any movement across the country quite difficult. This is especially the case for IDPs in Anbar province, who represent 40% of displaced people in Iraq. Many head to Baghdad, which has one of the highest IDP populations alongside Anbar, but some are unable to enter and remain trapped in Anbar province. In Anbar there is humanitarian presence due to the high security risks, which restricts assistance to IDPs there. Other IDPs from provinces such as Diyala or Salah al-Din tend to go to Kurdish areas and Kirkuk.
According to the International Organisation for Migration, 70% of IDPs are living in private settings, such as homes that they are renting, with families, or hotels; 19% are in ad-hoc buildings, and another 8% in camps.
Funding for Iraqi IDPs is also becoming an issue. The UN’s 2015 appeal for Iraq is still 90% underfunded, and because of this, it has had to shut down, or scale back, various programmes assisting IDPs. Such conditions are related to the decision by many displaced people to flee the country altogether, whether to Europe or elsewhere, seeing no prospects for improvement.
What is the attitude of the Baghdad government, ISIS, and the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) to those fleeing conflict in Iraq?
Regarding the attitudes towards IDPs, the government is worried about ISIS-linked infiltrators within refugee groups-especially in Baghdad which tends to have the highest number of monthly fatalities due to frequent bombings, many of which claimed by ISIS. Therefore the Baghdad government has implemented heavy restrictions and background checks, and the process often requires a long wait and sponsors. The Bzeibiz bridge between Anbar and Baghdad is mostly closed, according to UNOCHA, and only people who require medical treatment are actually allowed to cross into Baghdad.
The KRG is similar in that it is worried about ISIS operatives launching attacks in its territories, but it also cites economic reasons. The KRG says it is cash-strapped and doesn’t have the resources to deal with the influx of refugees. The situation is exacerbated by the KRG’s own rivalry with the Baghdad government; it feels that Baghdad is not sharing the burden. The political dynamics between the KRG and Baghdad are also affecting ‘contested’ areas such as Kirkuk, where the Kurds fear ‘Arabisation’ by IDPs and both sides are suspicious of one another’s actions in Kirkuk.
ISIS has tried to prevent people from leaving the territory under its control, placing explosives around cities, confiscating identity cards, and executing people who are caught trying to flee. Its bureaucracy has allowed people to leave in the past but under particular conditions, such as leaving their families hostage, giving up their homes, or paying large sums of money. ISIS is using the plight of the displaced people as a recruitment tactic. It uses images of Sunni IDPs struggling to enter Baghdad in its audio-visual material with the message, lamenting their inability to enter various provinces, including their own capital. It tries to depict itself as the only actor defending Sunnis and therefore they should to their homes in areas under ISIS control, or even volunteer to join the group.”
So Sunni people fleeing undermines ISIS’s image of a cohesive Islamic state-building project?
Very much so. And you can see this in recent propaganda videos directed at refugees leaving Iraq. A recent video urged refugees to join the ‘caliphate’, rather than fleeing to what it regards as a xenophobic Europe. Indeed, the fact that many people are fleeing ISIS contradicts the image of itself as a coherent state which it has been trying to project. Having people to govern over is essential for ISIS’s vision.
You mention at the end of your article that fleeing has become increasingly difficult because of a crackdown on internal resistance groups. How effective have groups such as the Mosul Brigade been and what types of resistance have they been putting up?
Information on resistance groups in Mosul is difficult to obtain and verify; this is the case with most of the information coming out of Mosul in general. That is why is it’s difficult to assess the impact or magnitude of such an internal resistance, or to speculate as to whether it is an organised resistance movement, Some claim they are coordinating with the Iraqi security forces and the coalition, but others appear to be individuals reacting to the violence perpetrated by ISIS or settling scores with ISIS fighters.
My guess would be that it is a combination of both. One of the main indicators that there is significant internal resistance in Mosul is that ISIS has actually instigated these heavy crackdowns in Mosul, executing hundreds of people (some sources have cited figures as high as 2,000). The make-up of those who have been executed is also telling: most are linked to the Iraqi security forces, who are thought to have been behind many of the attacks against ISIS fighters.
It has been exactly a year since the first UK airstrikes against ISIS in Iraq. How effective have these US-led air strikes in Iraq and Syria been?
The airstrikes on their own do not have a decisive effect, but combined with ground operations, they have assisted Kurdish groups in regaining significant swathes of territory in northern Iraq and restricting expansion by ISIS. In the operation against Tikrit in March 2015, for example, which was led by the Hashed al-Shabi militia, the belated airstrikes by the US-led coalition were in fact key in expelling ISIS from the city. The airstrikes have not been as effective in Syria, aside from assisting Kurdish groups in the north, such as the well-known battle for Kobani. This is linked to the more complicated dynamics of the Syrian crisis: there is a lot more happening than just ISIS.
What do you make of the recent Russian military commitment to Syria in order to support Assad supposedly against ISIS?
It is a disturbing development especially since the conflict contains many actors beyond Bashar al-Assad and ISIS, and, as you were suggesting, the first airstrikes didn’t target ISIS, but rather, rebel groups.
Tragically, I think this will most likely only enable the war to drag on longer, with severe humanitarian effects—ones that we already witnessing and that will not simply go away.
Away from Iraq and Syria, how much progress are ISIS making in areas such as Libya or Yemen?
In Yemen, ISIS-linked groups that have slowly emerged throughout the past year appear to be making progress in the chaos of the current war. A recent report from a journalist based in Aden noted that ISIS seem to be more organised than Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and has been successful in directing some of Al-Qaeda’s recruits and infiltrating its support bases. This is important because it suggests that the situation is changing. Earlier, ISIS-linked groups (which usually call themselves ‘Wilayet Sanaa’ or ‘Wilayet Aden’ or others based on the province) did not seem to be as organised as AQAP and were unable to challenge it. Most of the attacks by ISIS-linked groups in Yemen have been against the Houthi or Shia mosques in Sanaa, although there have been other smaller-scale incidents elsewhere, such as in the south.
In Libya, ISIS-linked groups are one of many groups vying for control, including various jihadi organisations and Islamist groups. ISIS-linked operatives have taken advantage of the chaotic war to establish a presence there and create a ‘jihadi front’ in North Africa—to which many foreign fighters have fled. It is important to emphasise that although the group has expanded due to foreign fighters, it has failed to gain many recruits from within Libya. So overall, within Libya’s military and political context, ISIS remains quite marginal.
In Egypt, the situation is different because there is a functioning state and a functioning army, but the ISIS-linked group, Wilayet Sinai in North Sinai has posed a serious threat, and its capacity has continued to grow, despite escalating crackdowns by the army.
While many of these groups have adopted tactics used by ISIS, such as beheadings, they don’t merely reflect an expansion by ISIS into these territories. Both sides effectively benefit from this partnership. ISIS can give the impression that it is unstoppable, undefeatable, and is everywhere. Its local affiliates - predominantly opportunistic groups – gain notoriety by leveraging ISIS’s name, which helps them win over recruits and possibly get funding or weapons. This is also discernible in who the ISIS-linked groups view as the main adversary in each of the different contexts, i.e. the army in North Sinai in Egypt, the Houthis in Yemen, and the Libya Dawn coalition in Libya.
In your opinion, how does a state like Libya which is effectively a failed state benefit groups like ISIS?
Armed groups such as ISIS thrive in that atmosphere of a political and security vacuum, and their emergence is fundamentally linked to the state of war. This state of war provides obvious logistical advantages, such as the ability to smuggle foreign fighters into the country, and the lack of a functioning security apparatus enables them to organise, expand, etc., but they also benefit from the political reasons that lead to the descent into a failed state. ISIS-affiliated groups, as I mentioned, are not created by ISIS, but are informed by the political crises governing each of the countries.
Thank you.
Jack Curran-Persell is currently completing an MA in Conflict, Security, and Development within the War Studies Department at King’s College London.