By Victoria Fontan: Dr. Victoria Fontan writes this article from Duhok, Kurdistan.
Dr. Victoria Fontan writes this article from Duhok, Kurdistan.
EDITORS NOTE: On May 20, following the publication of this article, the Iraqi government granted conditional entry to Baghdad for IDPs fleeing the violence in Ramadi. However, as of May 22, Sharqia News, Iraqi TV was reporting the bridge had only been opened for 1,000 IDP’s, leaving 5,000 remaining IDPs stranded.
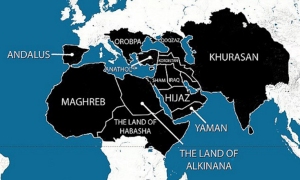
The town of Ramadi has completely fallen to the Islamic State in Iraq and Sham (ISIS). Many commentators have already stated that this is a major defeat for the government of Prime Minister Abadi. Indeed, it represents both a long and short-term disaster for the current Baghdad administration.
Only a month after triumphantly proclaiming that he would rid Anbar of ISIS, against US wishes to focus on re-taking Mosul, Prime Minister Abadi has failed. His strategy is not only placing Baghdad at risk, but also the Haditah Dam, the second largest source of hydropower in Iraq.
Shi’a militias are now gathering in Habaniya airbase in preparation for a major counter-offensive. Yet, a year on, Mosul is still waiting to be “saved”. This flexing of governmental and Shi’a militia muscles seems to be no more than a Baathist-style propaganda stunt, that former Saddam Information Sahhaf-style. So what does this mean for Iraq?
It is now very clear that the modern state, as Gertrude Bell designed it, belongs to the history books. Sectarian relations between Iraqi Sunnis and Shi’as have reached a point of no return. Conflict resolution scholars compare relationships to an elastic band: it can be stretched, but at one point, it breaks.
Baghdad’s refusal of Anbar Internally Displaced Persons (IPDs) illustrates this. While the Kurdistan Regional Government welcomed almost two million Arab IDPs after the fall of Mosul last June, Baghdad has closed its doors to its own, clearly indicating to the its Sunni population that Iraq is no longer their country.
With this clear sign of sectarian disintegration of the country, Kurdish independence looks like a fait accomplit. It is not a matter of if, but when Kurdistan will finally exist as a sovereign State. Seen under this light, Kurdistan is indirectly benefiting from Prime Minister Abadi’s strategic and sectarian mistakes. That is a clear long-term benefit to Kurdistan, but at what price?
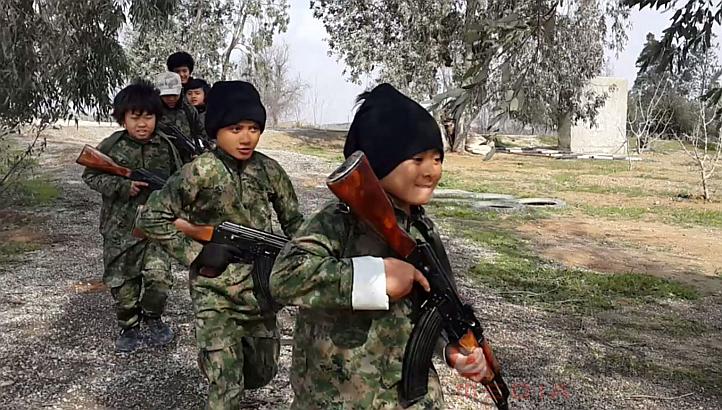
In the short term, it might be that once again, Baghdad’s errors have to be paid for by the Kurds, and specifically the Peshmerga forces, who remain, under-armed, in the northern frontline of the war against ISIS. In the same way that ISIS significantly benefited from the fall of Mosul in terms of weaponry; scores of armaments were left when General Berwary and his Golden Brigades left the Anbar Military Command on Sunday.
Like the Baghdad-backed Shi’a militias, ISIS is armed with the latest technology; while Peshmerga only receive a fraction of the weapons sent by the US via the Baghdad government. This makes the holding of frontlines, such as in the town of Sinjar, which I visited a couple of weeks ago, more difficult.
This also undoubtedly reinforces an unnecessary metric imbalance between ISIS and the Peshmerga. Each time that the Baghdad Government makes another gross mistake, its ripple effects can be felt at the largest frontline against ISIS, defended by the Kurds for over 1000 kilometers. Each Baghdad military defeat creates even stronger anti-bodies in the ranks of ISIS, whose fighters, thanks to the government’s strategic mistakes, have access to the latest weapon technology. With the strategic help of former Iraqi Army top commanders, the combination is proving deadly on the battlefield. If it weren’t for the Coalition airstrikes, ISIS would have made more advances.
The results are instructive. In Tikrit, Abadi’s troops were incapable of retaking the city on their own. While more than 30,000 troops surrounded Tikrit for over a month, it was only after Coalition airstrikes and the Jibouri tribe’s assistance in re-taking the neighboring town of al-Alam, that the city could be accessed. How many ISIS bodies were found inside? Between 60 and 80. In Ramadi, it was reported that 6,000 Iraqi forces fell to 150 ISIS fighters. At this rate, the Iraqi army and Shi’a militias are only making matters worse.
Militarily, the Baghdad government has reached such a low that a sustained presence on the battlefield will only weaken its army even more, and further alienate the Sunni tribes who are still part of the coalition against ISIS. Politically, the Baghdad government should swallow its pride and start working on a serious end to sectarian politics in Iraq.
Dr. Victoria Fontan is the Interim Chair, Department of Politics and Public Policy, at the American University of Duhok, in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. She is also the author of “Decolonizing Peace” (2012) and “Voices from Post-Saddam Iraq” (2008). She is now undertaking an additional PhD in the Department of War Studies, King’s College London. Her thesis title is: “The Resilience of Insurgencies in Fallujah.” You can find more information on Victoria Fontan’s research on her website: http://www.victoriacfontan.com or follow her on Twitter @DecolonizingPAX.