By Axel Dessein
30 October 2018
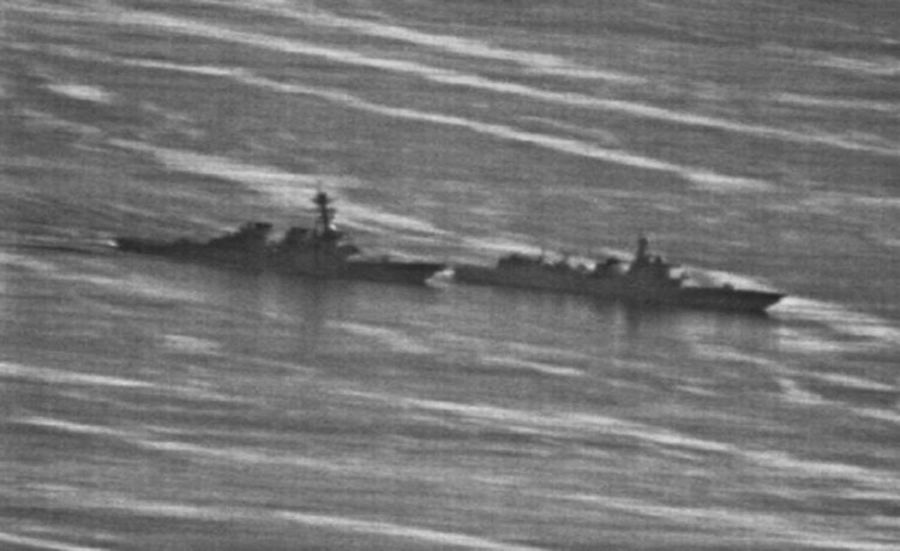

In late September 2018, a Chinese Luyang-class destroyer nearly collided with the American destroyer U.S.S. Decatur during a Freedom of Navigation Operation (FONOP) in the South China Sea. These operations are essentially aimed at signalling a commitment to keeping the sea lanes open, the near-collision demonstrates that such commitments are to be upheld. Following the unsafe encounter at sea, several commentators pointed out that this atypical event may be a reflection of the broader deterioration in relations between the two countries. Indeed, we may now be witnessing the effects of the trade war spilling over into the military and security domain. This shift in behaviour is a crucial development, as the Trump Administration seems to have declared a new Cold War on China.
Winning Control
At the strategic level, China’s acquisitions in the South China Sea are its answer to the First and Second Island Chains, which caused the country’s claustrophobic vision of its surrounding seascape. Indeed, while the American interpretation of these island chains was aimed at keeping the country in, China itself views this enduring element of the region’s geostrategic outlook as benchmarks for its naval ambitions, as Andrew S. Erickson and Joel Wuthnow demonstrate.
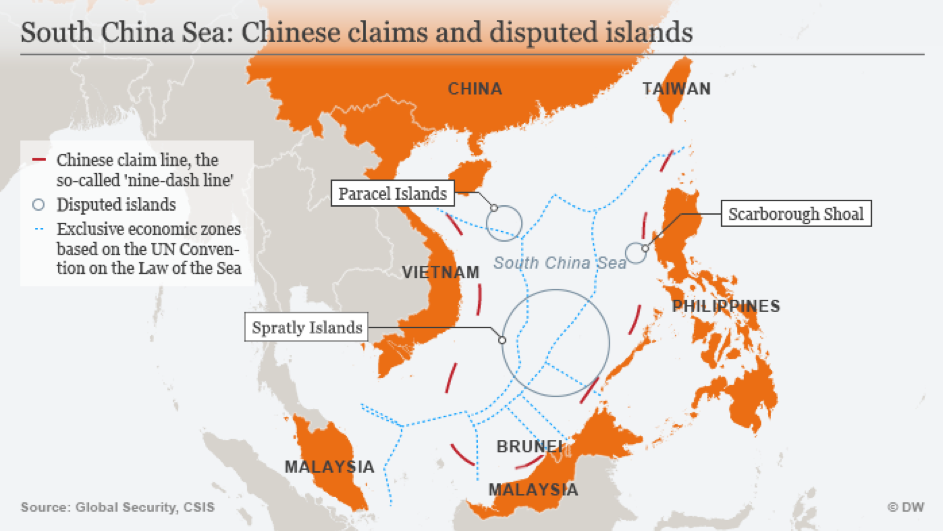
In the 1970s, China took control of the Paracel Islands and their surrounding waters after a military standoff with the Vietnamese Navy. It is on those islands that China eventually established Sansha City, the administrative basis for control over the “Three Sands:” the Paracels (or Xisha, West Sand), the Spratlys (or Nansha, South Sand), and the Macclesfield Bank and Scarborough Shoal (commonly grouped under the name Zhongsha, Central Sand).
Undoubtedly, heaps of sand abound. Satellite imagery reveals that since 2014, China has engaged in massive land reclamation and construction activities on many of the islands and submerged features. This island-building enterprise is a clear expression of the intent to establish a military foothold in the region, thereby securing relative control of the sea. If for instance, one draws a line between the different island groups, a triangle becomes visible within the Nine-Dash Line, a series of dashes that trace China’s maritime demarcation line.
The Science of Military Strategy (Zhanlüe xue), an informative study released by the Chinese Academy of Military Science is especially enlightening as to what these advancements mean for China. According to the study, China’s strategic thinking is increasingly looking towards the South China Sea to attain a form of effective control (youxiao kongzhi) over the area to establish a forward-deployed position (qianyan fangwei) away from the mainland. However, it remains unclear what exactly China is claiming: the sea itself or the many features within the Nine-Dash Line.
This ambiguity fits perfectly within the nature of the country’s approach towards asserting its claims. In fact, China seems to be moving within the so-called grey zone, a form of strategy “at the low end of the conflict spectrum in which […] military coercion is occurring to alter the status quo,” according to James J. Wirtz. Whether conflict in the grey zone is an entirely new domain is of course an interesting debate, as Toshi Yoshihara demonstrated an earlier variation of such behaviour in his appraisal of the Paracel Sea Battle between China and Vietnam. Whatever the answer may be, such short-of-war behaviour has clearly demonstrated its effectiveness time and again.
Manning the Great Wall at Sea
Ambiguity and non-military coercion appear to be essential elements in China’s toolbox for the South China Sea. Conor M. Kennedy and Andrew S. Erickson have written extensively on this topic. Most importantly, one has to recognise that there are essentially three Chinese sea forces: the grey-hulled navy, the white-hulled coast guard and its fishermen. Aptly called a maritime militia, these fishing boats are the vanguard involved in promoting and defending China’s sovereignty at sea. That is not to say, however, that China has come up with a recipe for success.
The 2012 Scarborough Shoal standoff demonstrates the fallibility of Chinese strategy. Special attention can be drawn to the Philippines which in 2013 filed a case against China’s territorial claims at the Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague. After a ruling in favour of the Philippines that thereby denied the Chinese claims, China rejected the validity of the PCA and insisted on resolving the disputes bilaterally. In this instance, China failed to win control, and the shoal remains a major source of tension between the two countries.
Other attempts have been made to quell China’s expansionist activities in the South China Sea. After sixteen years of negotiations China and the Association of the Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) recently made some progress on drafting the framework of a proposed Code of Conduct in the South China Sea, which is a slow albeit necessary process. However, the conflict is not limited to Asia. Because of the growing economic and political relationship between China and countries like Greece, the European Union has come short of wording a clear statement on the issue. Here, we see attempts at preserving international law in a key trading region like the South China Sea increasingly being trumped by other economic interests.
One commentator suggests that the Scarborough Shoal standoff reveals much about China’s intent. The country demonstrated non-military assertiveness with the aim of becoming a great power at sea (haiyang qiangguo). Another commentator sees an analogy between China’s sea power endeavours and those of the German navy under Admiral Tirpitz. Broader historical parallels are also drawn with the Anglo-German conflict of the nineteenth century. However, while the clash between the world’s most powerful states is primarily about their desire for great-power status, diverging ideologies are shaping how this conflict plays out. Here, Alfred W. McCoy writes: “Treat the South China Sea as central, not peripheral, and the Cold War not as bounded by a specific ideological conflict but as the midpoint in a century-long clash of empires.” Today, the empires in question are of course, China and the U.S.
A Relationship Adrift
Amid growing trade tensions, the countries put a halt to their Diplomatic and Security Dialogue (D&SD). The U.S. Secretary of Defence James Mattis also skipped China during his October 2018 trip to Asia, but did meet with his Chinese counterpart in Singapore. In light of such events, it is but a small surprise that Chinese academics and political groups are discussing a “decoupling” (tuogou), a process which describes a potential rupture in the economic and security relationships between China and the U.S. The risks associated with such an unravelling of the ties between China and the U.S. are manifold, with increased tactical instability demonstrated by the recent near-collision as an example.
Strategic competition with China is back on the American agenda. As a result, the two giants are increasingly stepping on each other’s toes. In this scenario, the destroyer’s sortie could indeed be a display of greater confidence and boldness on the Chinese part, showcasing a broader shift in the relationship. Nevertheless, it is interesting to note that an article by a think tank affiliated with China’s State Council still urges restraint in face of “long-term strategic competition” with the United States. While it is unclear how long such moderation will last, our understanding of the Chinese decision-making process clearly suffers from large information gaps. Simply talking about a new Cold War will not be the answer, learning from Chinese words and actions will be.
Axel Dessein is a doctoral candidate at King’s College London and a Senior Editor at Strife. His research focuses on the implications of China’s rise on the current world order. Axel completed his BA and MA in Oriental Languages and Cultures at Ghent University. You can follow him on Twitter @AxelDessein.
Banner image source: https://www.stripes.com/news/photos-show-how-close-chinese-warship-came-to-colliding-with-us-navy-destroyer-1.550153